Artificial Intelligence (AI) is something that freaks out many people, especially after Elon Musk famously said in 2018 that it is “far more dangerous than nukes” for the human species.
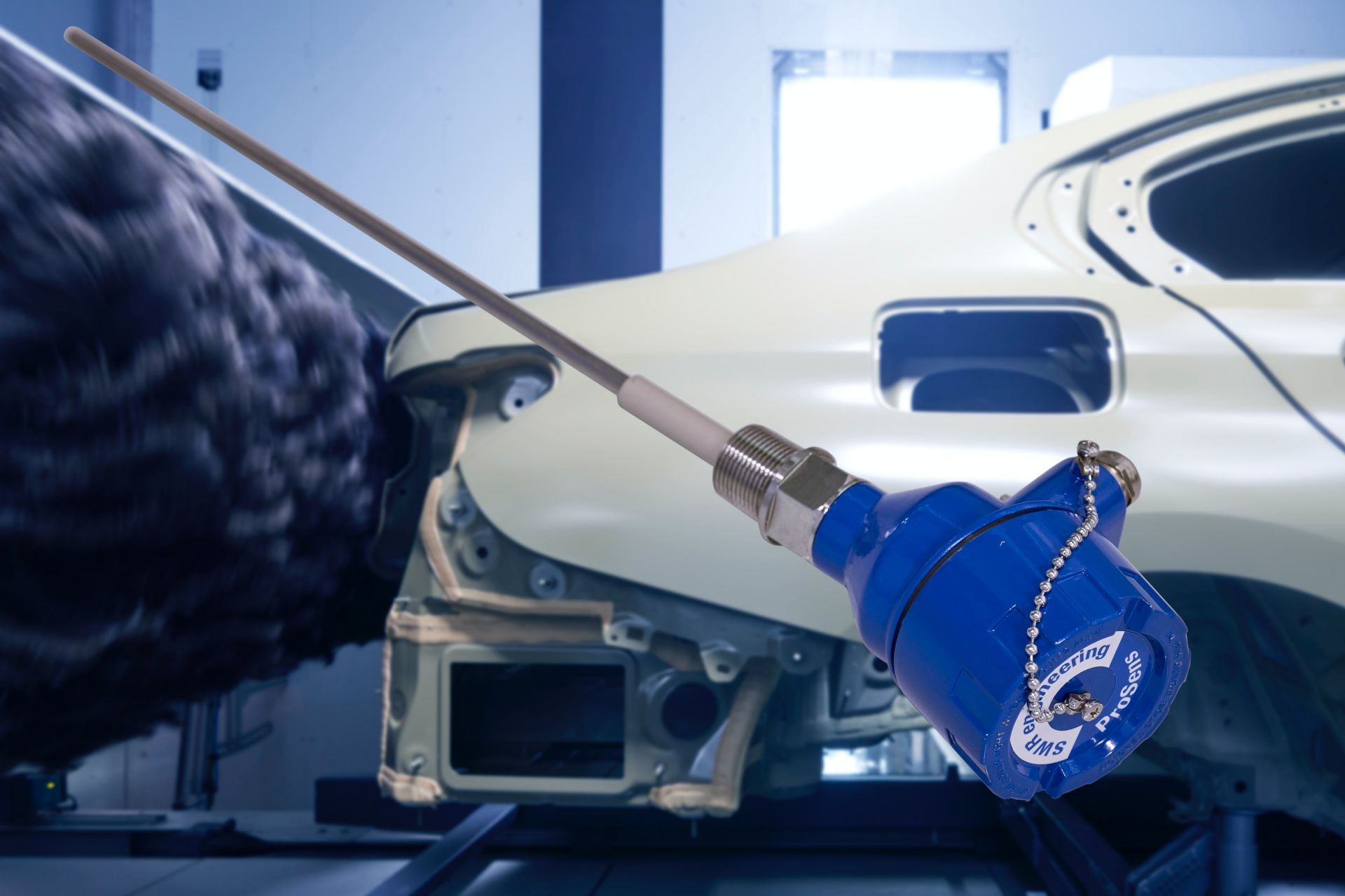
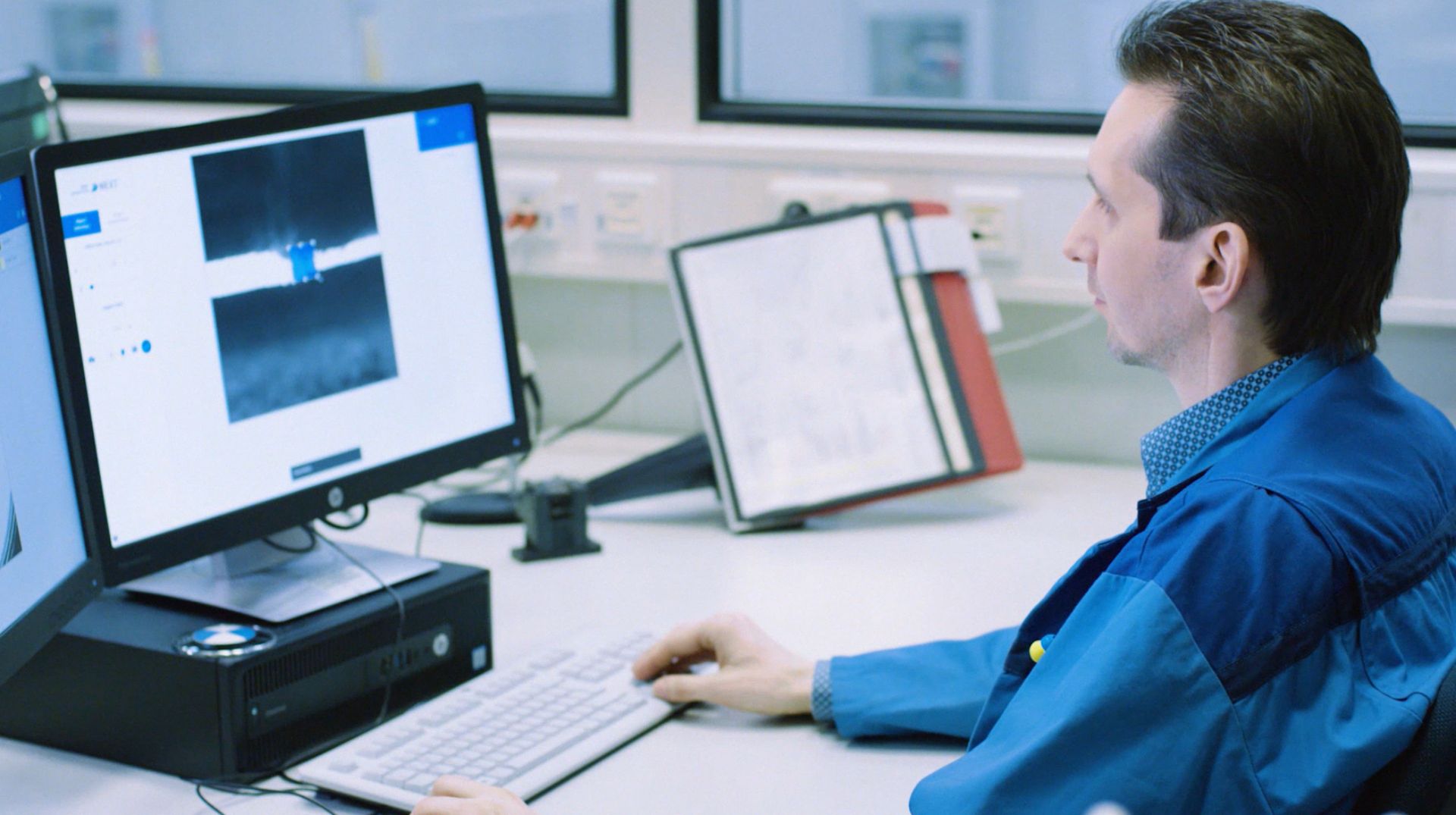
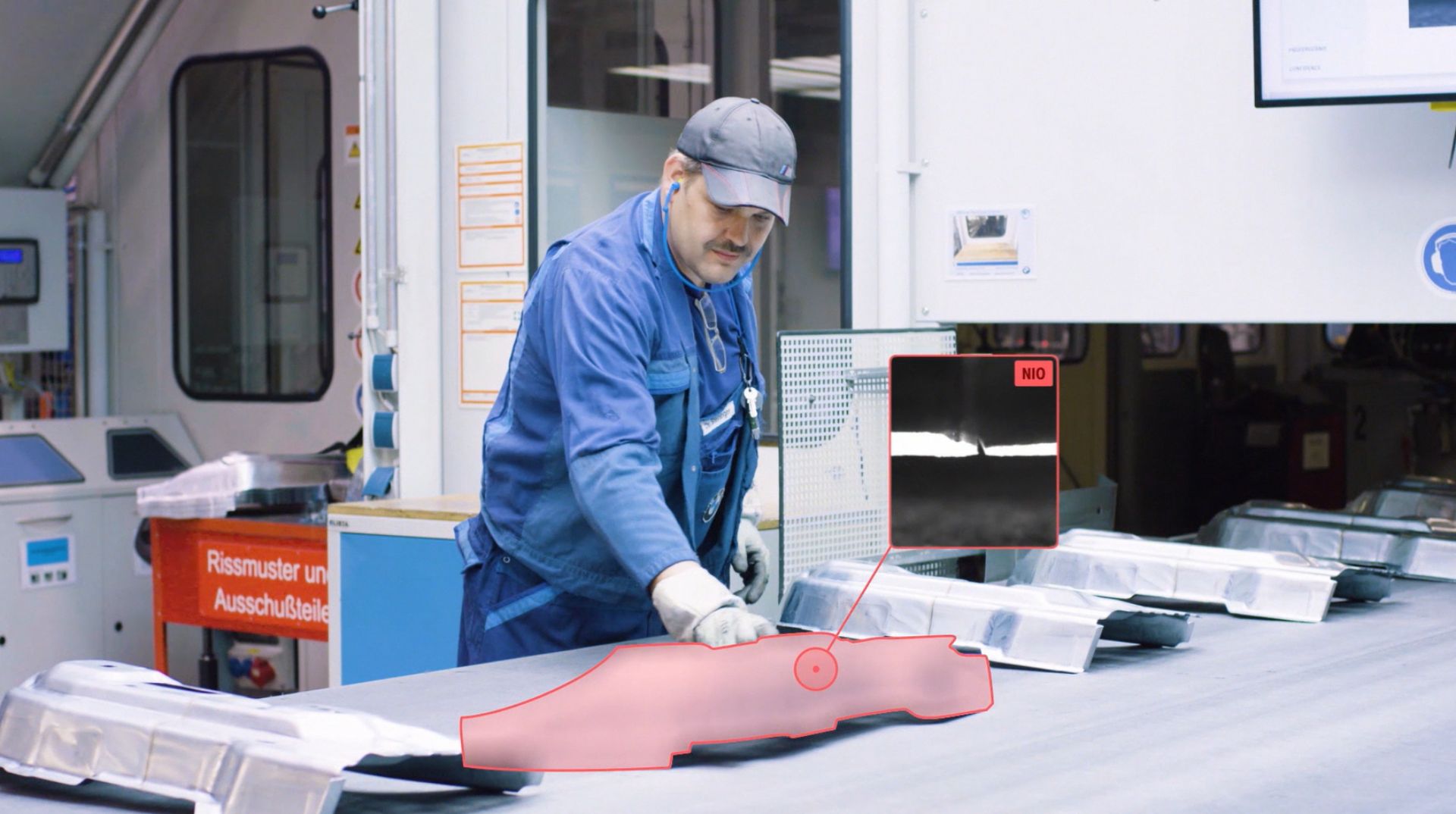
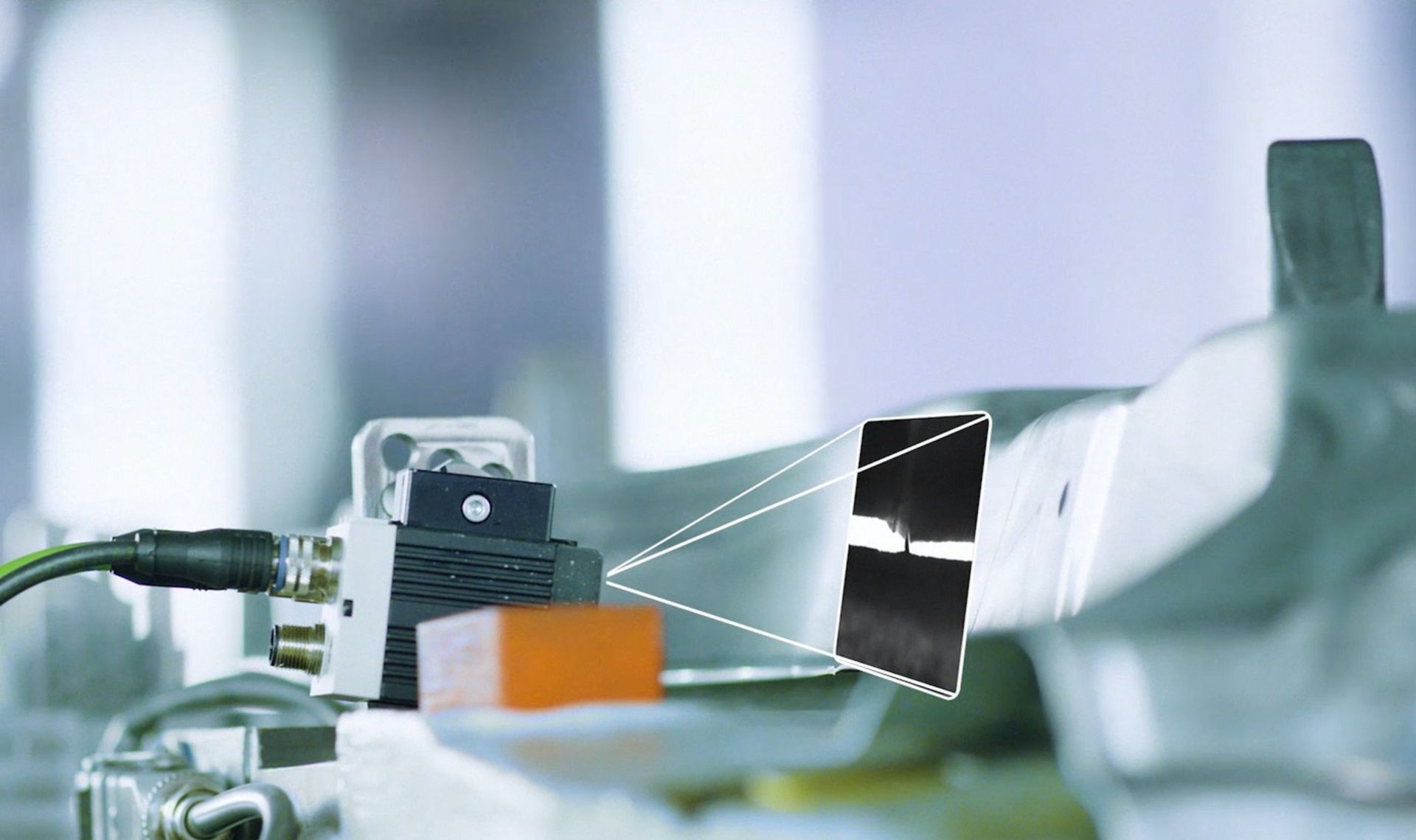
While some people are wary of the ever-increasing presence and power of AI, companies fully embrace the benefits it brings. The BMW Group makes no exception and says AI is already widely used within the company, with over 400 use cases throughout the value chain. However, the German automaker aims to keep AI on a tight leash, as it has set certain boundaries for AI use.
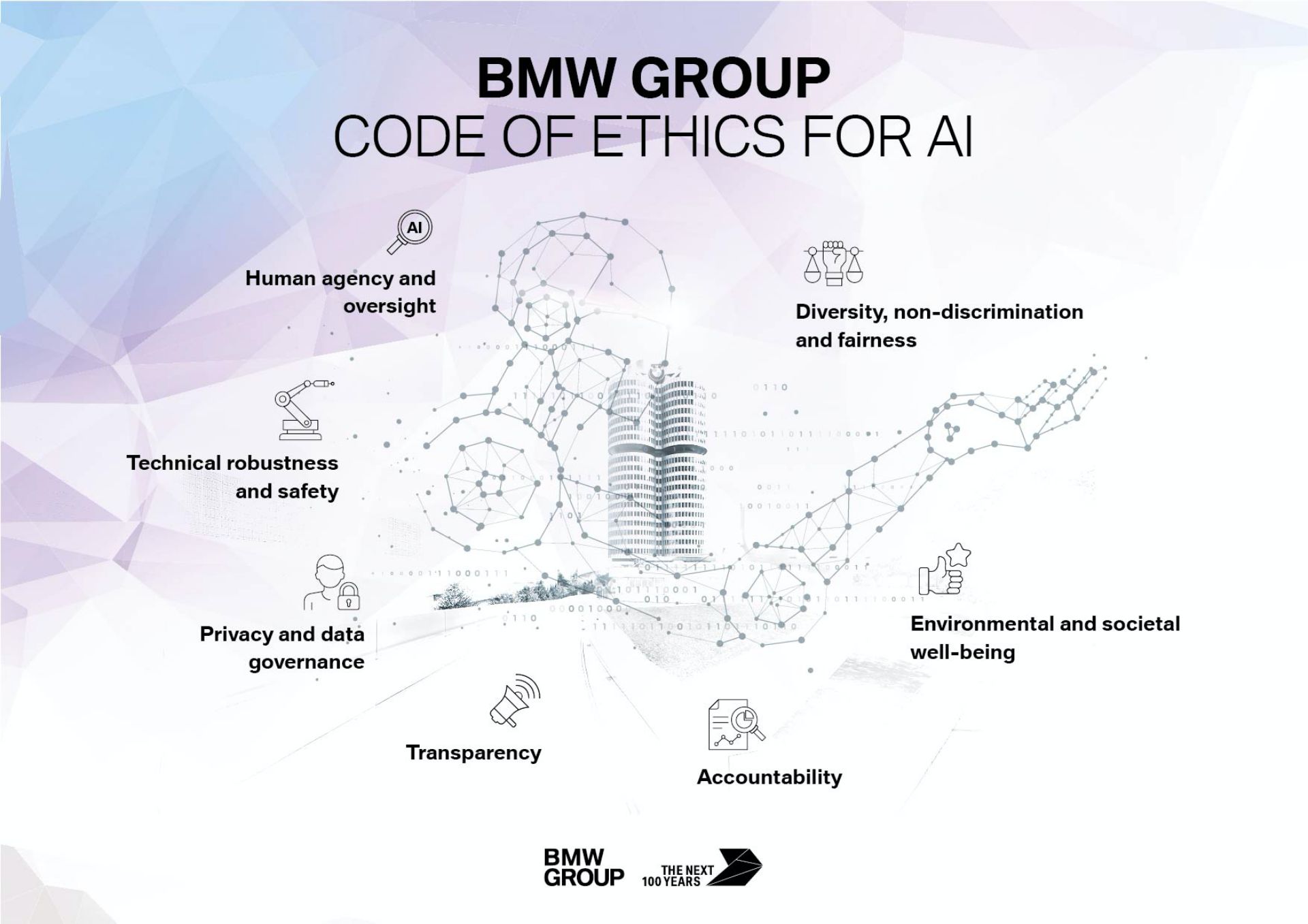
More specifically, BMW Group has elaborated a code of ethics for the use of artificial intelligence. “We are proceeding purposefully and with caution in the expansion of AI applications within the company. The seven principles for AI at the BMW Group provide the basis for our approach,” says Michael Würtenberger, Head of “Project AI”.
Read Also: Hyundai Working On World’s First AI-Based Cruise Control Tech

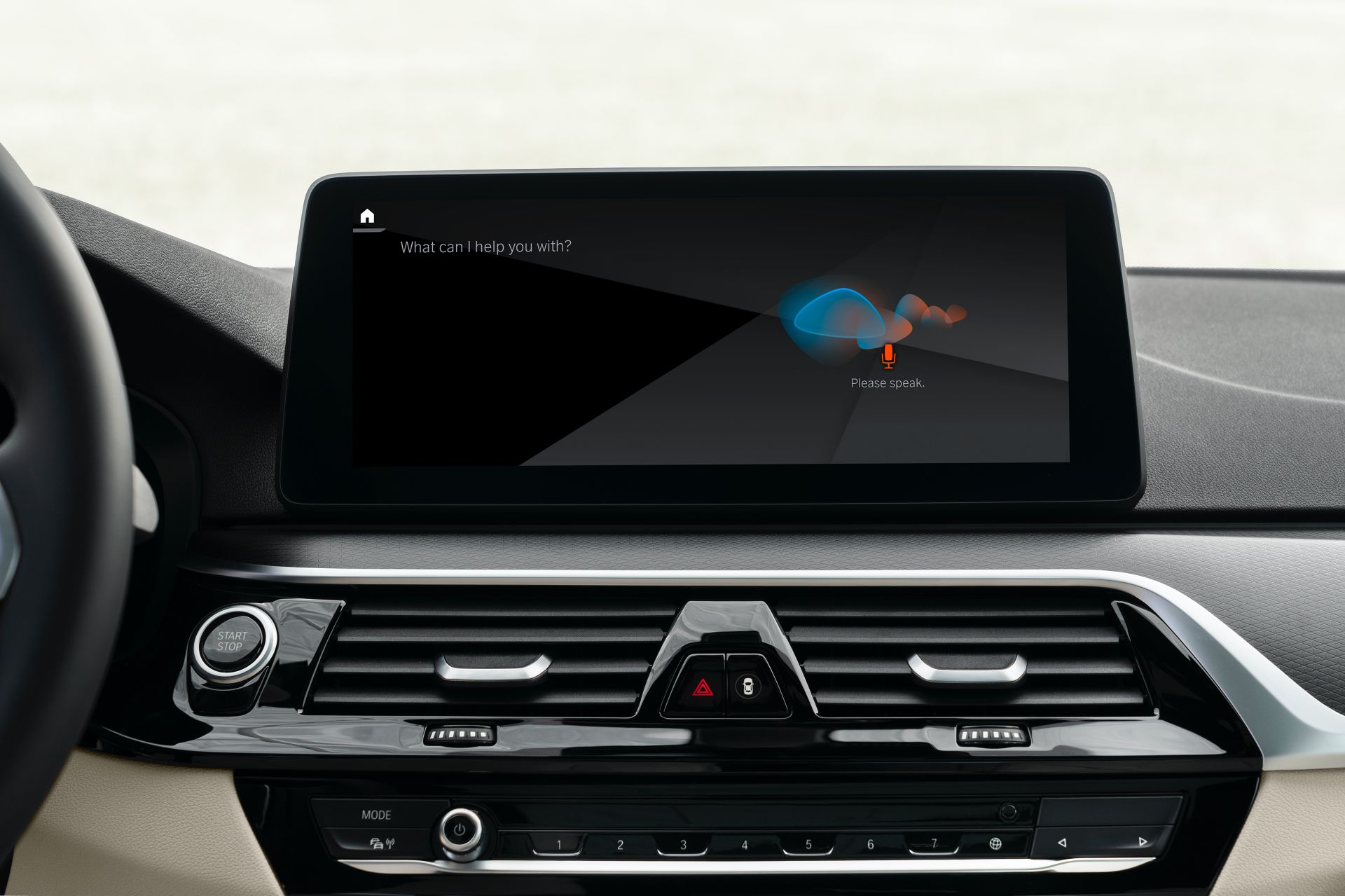
The BMW Intelligent Personal Assistant is one of more than 400 AI applications used within the company
While artificial intelligence is the key technology in the process of digital transformation, BMW says its focus remains on people, with AI’s roles being to support employees and improve the customer experience. That said, the BMW Group and other companies and organizations are involved in shaping and developing a set of rules for working with AI, with the company taking an active role in the European Commission’s ongoing consultation process.
The automaker has worked out seven basic principles covering the use of AI within the company, building on the fundamental requirements formulated by the EU for trustworthy AI. The principles will be continuously refined and adapted as AI is applied across all areas of the company.
The first and probably most important principle is “Human agency and oversight”. This means that the BMW Group implements human monitoring of decisions made by AI applications and considers possible ways that humans can overrule algorithmic decisions.
The second principle, “Technical robustness and safety”, is about developing robust AI applications and observing the applicable safety standards “to decrease the risk of unintended consequences and errors.” “Privacy and data governance” is the third principle which refers to BMW extending its data privacy and data security measures to cover storage and processing in AI applications.
Another essential principle is “Transparency” as the BMW Group aims for “explainability of AI applications and open communication where respective technologies are used.” The fifth principle, called “Diversity, non-discrimination and fairness”, is based on the fact that the BMW Group “respects human dignity and therefore sets out to build fair AI applications.” This includes preventing non-compliance by AI applications.
“Environmental and societal well-being” is another principle which commits BMW to developing and using AI applications that promote the well-being of customers, employees and partners. Finally, the “Accountability” principle stipulates that the automaker’s AI applications should be implemented so they work responsibly. “The BMW Group will identify, assess, report and mitigate risks, in accordance with good corporate governance,” the company says.